The key difference between our Earth and other planets of the solar system is the presence of biological objects on it. As a result, the life cycle, which has been going on for billions of years, is not only the unique heritage of our planet but also the basis of the carbon energy we use (oil, natural gas, etc.).
However, at present, the impact of the use of carbon - based energy sources on global warming has become an indisputable fact. Therefore, turning to alternative energy sources is an inevitable path for our future.
The fact that environmentally friendly green energy sources that have been developed in recent years are becoming more efficient is promising in terms of reducing the carbon dependence of our planet. One of the most important technologies that stand out in the race for sustainability and recycling, undoubtedly, is biogas energy.
Biogas energy is energy produced by using plant and animal waste. That is, what remains of biological life on our planet is converted into electricity. Today, biogas production can be carried out at various scales, from covering the energy consumption of a single house to the mass generation of electricity using generators. Let's take a look at how this happens together.
How Is Biogas Energy Produced?
Biogas is produced in three stages. These are hydrolysis, acidification, and methane formation.
Hydrolysis
This is the stage of the formation of volatile fatty acids. Fermentation and hydrolysis bacteria decompose the three main parts of organic matter (proteins, carbohydrates, and fats) into carbon dioxide, acetic acid, and soluble volatile organic substances, mainly fatty acids.

Acidification
Acidification releases the acetogenic (acid-forming) bacteria released in the hydrolysis step to convert volatile fatty acids into acetic acid (an organic acid). Some bacteria combine with carbon dioxide and hydrogen to form acetic acid. It is less effective comparing to volatile fatty acids.
Acid-forming bacteria convert soluble organic matter into smaller anaerobic substances such as acetic acid, volatile fatty acids, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. Anaerobic substances are bacteria that cannot survive or reproduce in the presence of oxygen. These substances need an acidic environment, oxygen, and carbon to develop. Acid-forming bacteria also provide the anoxic environment required by methanogenic bacteria.
Acid production takes less time than methane production. When there is a sharp increase in the concentration of organic matter, acid formation increases, and the pH value decreases. Therefore, acid-forming bacteria have an inhibitory effect on methane bacteria.
Methane Formation
The last step in the process is methane formation. At this stage, methanogens, namely methane bacteria, enter the scene. Some of those bacteria use carbon dioxide and hydrogen to create methane and water. Others use the acetic acid from the acid formation step to form methane and carbon dioxide.
The process of methane formation differs depending on the type of wastewater and waste organic matter and occurs at different temperatures.
- For psychrophilic bacteria: 5-25°C
- For mesophilic bacteria: 25-38°C
- For thermophilic bacteria: 50-60°C
After the successful completion of all three stages, biogas energy is released. When using this energy, the plant is of the greatest importance.
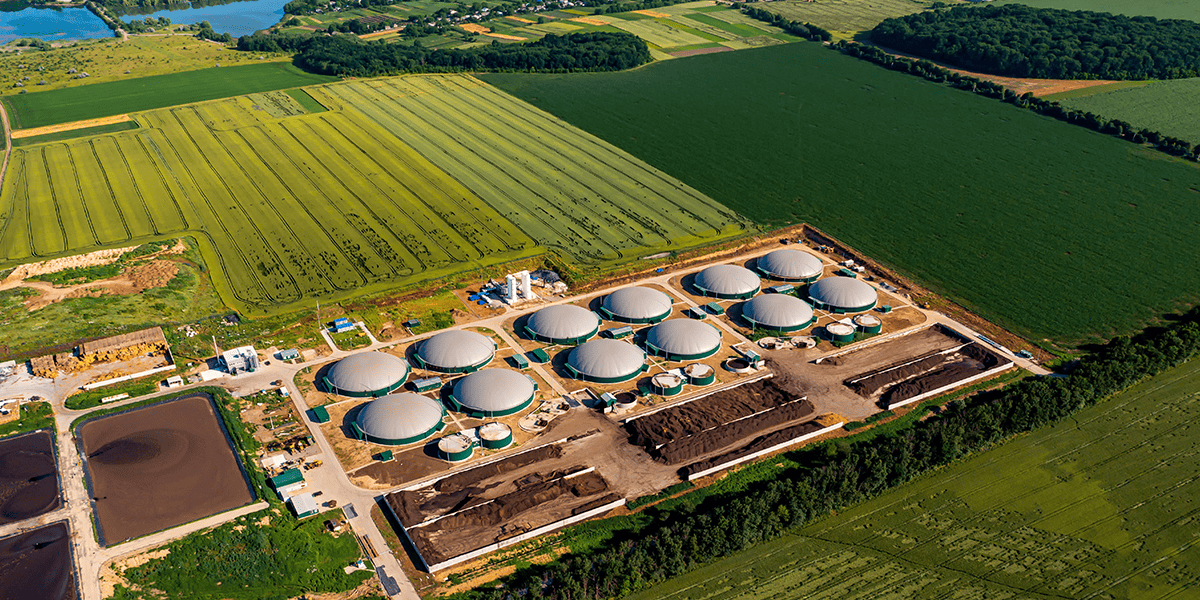
What Is a Biogas Plant, And How Does It Work?
Biogas plants actively purify nature. Here, biogas and organic fertilizers are being produced from waste. These facilities are of key importance in the fight against climate change, as they prevent the release of methane gas into the atmosphere, which has the greatest impact on global warming.
In the biogas plant, the required feedstock, after being fed into the pre-balancing pool, is mixed with a mixer. Thanks to this process, precipitation is prevented, and the waste entering the reactor is homogenized. The raw material is moved from the balancing pool to the biogas reactor and heated to the operating temperature by heating pipes. The biogas obtained in the reactor is sent to gas storage facilities, from there to gas generators, where it is further converted into electrical energy.
As Borusan Cat, we continue to be the pioneers in the sector by following innovations in the biogas field. We continue to offer “turnkey” solutions for our customers in terms of gas treatment (desulfurization systems, dryer, pressurization units) and production (biogas generator, heat recovery systems, auxiliary equipment, control system) in biogas plants, with a level close to 105 MW which we have achieved in recent years. As a result of our projects, we generate enough electricity to meet the energy needs of 257,000 homes a year.
We continue to create solutions for both our customers and our planet, using our approach to sustainability and the digital way of doing business.









Hello!
As writers for theBClog, we share with you articles that highlight current developments and inspiring ideas in various topics, from sustainability to technology, energy to climate, and innovation to human interest stories.
Enjoy!